New functionalities were introduced in version 12.0, providing the user with much finer control and customization of key features, specifically with the capability of locking clusters and concentration values in place, as well as the possiblity of providing custom calibrations for cluster center limits.
Details are provided in the sections below.
By default, the minimal transform windows on each side of peak cluster is set to 0.02 ppm, even if the pH equations predict a smaller value. It was put in place to account for possible matrix effects with some biological samples, among other things.
You can change this value in the software Preferences under the General tab. Modifying this value affects all clusters and has consequences on the capacity of the software to automatically position clusters. Contrary to manual peak positioning where going outside the calibrated transform window is allowed, calibrated transform windows are strictly respected during automated procedures, unless instructed to do so with a external custom calibration file (see below).
Compound concentrations can be locked so that their values cannot be changed by automated procedures or accidently by manual manipulations. Compounds will locked concentrations will appear green in Profiler's compound table.
You can activate the display of the lock statusus of compounds by right-clicking in one of the table column and selecting "Concentration locks". A column with a lock icon will appear. Clicking the lock icon will toggle the lock status on/off.
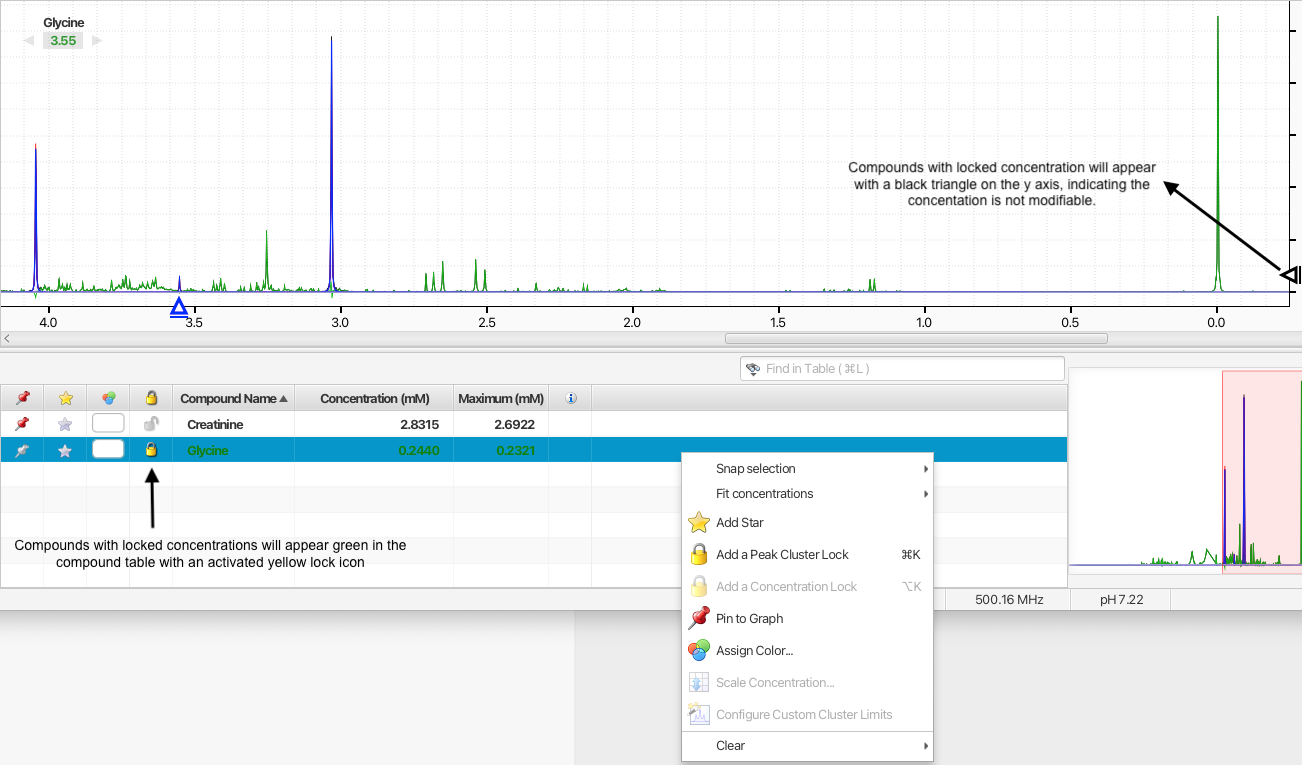 |
Alternatively, you cam choose to add or clear concentration locks on one or more compounds at once by first selecting the compounds in the compoudn table and then right-clicking on one of the compound's associated rows in the and choosing the appropirate otion. You can also directly add or clear concentration locks using keyboard shutcuts.
You can add or clear concentration locks to a whole series of spectra automatically via Tools Menu > Batch Operations > Batch Edit. (Pro version only)
Compound with locked concentrations will appear with a black triangle on the y axis. The triangle will not be movable until the concentration is unlocked.
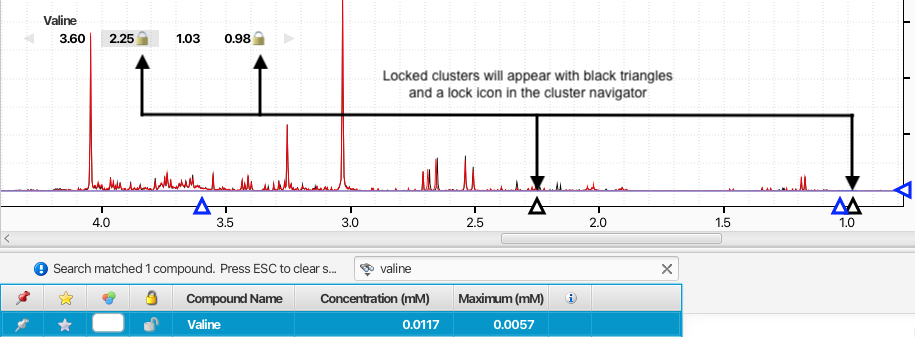
The positions of peak clusters can be locked in place so that their positions will not be modified by automated procedures or accidently by manual manipulations. Locked clusters will appear with a lock icon in the compound Cluster Navigator when the compound is selected.
You can toogle on and off the lock status of a cluster by holding on the command (Macintosh) or alt key (Windows and Linux) while double-clicking on its displayed location in ppm in the Cluster Navigator. Alternatively, you can select a compound and one or more of its clusters from the triangles displayed on the ppm axis, and right-clicking on one of them, or directly via the associated keyboard shutcuts.
Locked clusters will appear with a black triangle on the ppm axis and they will not be movable until they are unlocked.
 |
For the batch snapping, Legacy Autofit and the COMPLETE Autofit procedures, you can optionally overwrite the automatically calibrated peak cluster transform windows with your own set of custom values. They must be provided to the autopmatic routines via a tab-seperated value (tsv) file.
To define custom cluster limits values for a given cluster, activate the cluster from its associated triangle on the x axis, right-click and select Configure Custom Cluster Limits.
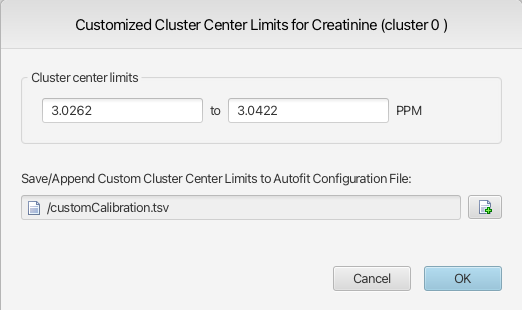 |
Provide custom values for the lower and upper cluster center limits, as well as a new or existing file to which the cluster information will be saved. By default, the values presented in the interface are the calibrated limits of the cluster center for the selected cluster in the currently opened spectrum if no spectral region has been selected prior to calling the function. On the other hand, if a region was selected, the limits of the selected spectral region will be shown. The default selected file will always be the last one used, allowing for fast additions to a growing file.

